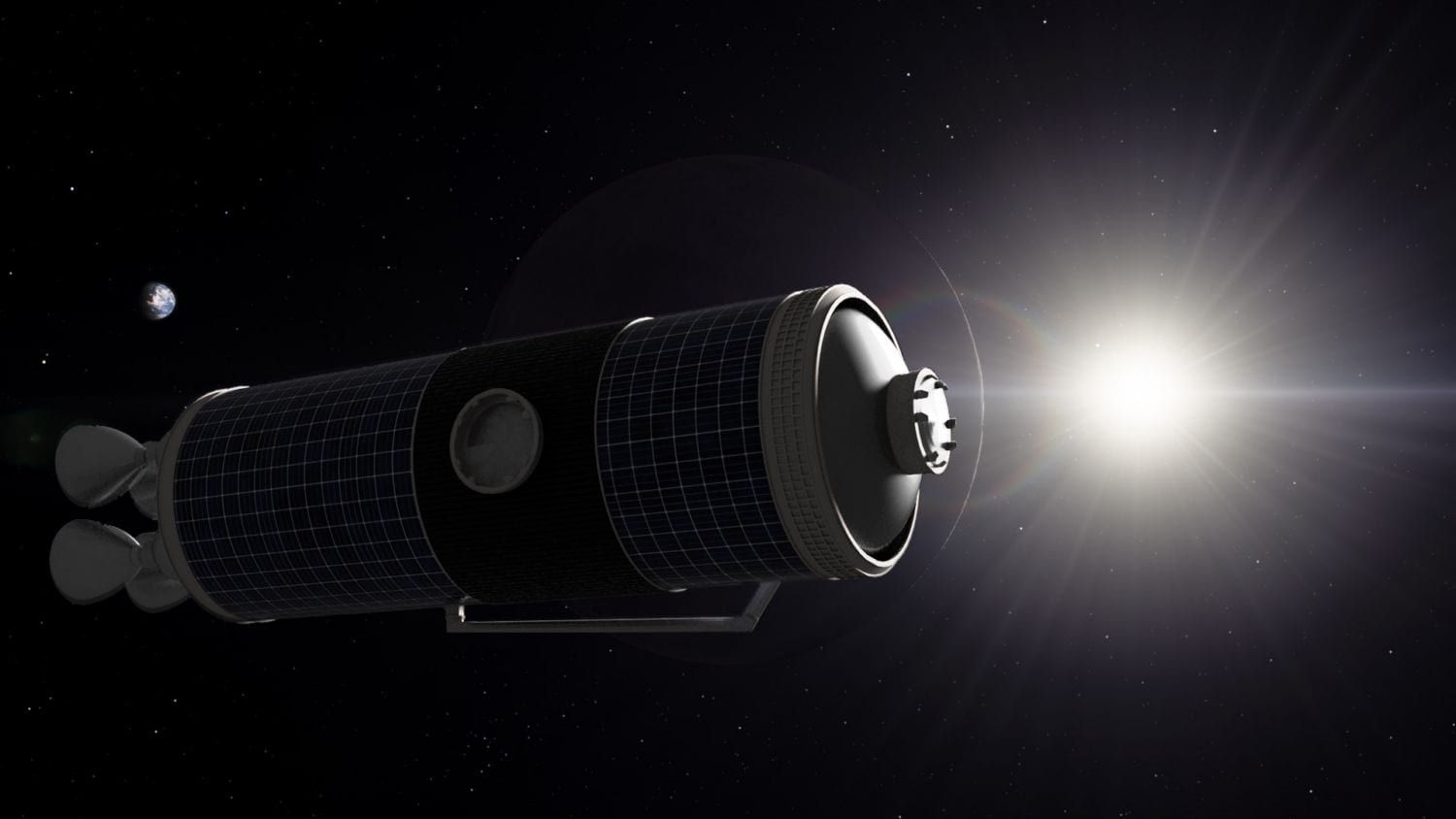
A rendering of a Nanoracks Outpost, make from the invested higher stage of a launch auto. Nanoracks
It is been far more than 70 yrs because the first rocket blasted off into space and 20 a long time considering that the very first human lived on the Global Place Station. These days, the ISS is speedily growing old, while the quantity of rocket missions is soaring, an remarkable advancement that is nevertheless creating a rising trail of house debris. In accordance to Nanoracks, a private house organization frequently delivering payloads to the ISS, one difficulty could just be the answer to the other.
“Right now, a rocket launch can expense anyplace from $50 million to $70 million. If we can demonstrate that you can prolong missions, then you are leveraging present assets and not paying out for a full launch,†Jeff Manber, founder and CEO of Nanoracks, stated to Observer.Â
For the earlier handful of decades, Nanoracks has been performing on a application known as Outpost, which aims to modify a rocket’s upper stage soon after it is done with its main mission. It then gets a miniature place station for scientific investigate, gasoline resupply and even area tourism.
The thought isn’t new, but no enterprise has taken concrete ways to test the systems required to make it occur. Previously this thirty day period, Observer spoke with Manber and David Marsh, the strategic lead of the Outpost program, about how Nanoracks options to convert useless rocket sections into some thing practical for future space (and Earth) missions.
I want to recognize the issue you set out to fix initially. Why are lifeless rocket phases a trouble? How are they distinctive than other space particles, say, satellites?
Jeff Manber: Two items could transpire to a rocket’s upper stage following start relying on the mission profile. If it is a low Earth orbit mission, the second phase will get burned up in the atmosphere. But if it is a deeper mission, like likely to the moon or someplace else, the 2nd stage is place in what’s termed a “graveyard orbit†and becomes a piece of house junk.
So we assumed we could make some of that hardware beneficial yet again. A rocket’s second stage can store a whole lot of energy, a lot far more than a satellite. It also has a large amount of interior space, so you could use it for production and lots of other uses.Â
David Marsh: This has been an strategy in the place earth for many years. I assume the initial proposal for converting rocket phases into space stations was from the ’60s or ’70s. What tends to make it probable now is the availability of business off-the-shelf equipment and know-how enabling that devices to do points in space.
How do you evaluate if there’s a market place for that?Â
Manber: Right now, we have an getting older global area station and this outstanding ecosystem becoming produced in decrease orbit for doing much more issues for place and also for Earth. People will require a lot of personal place stations that can be used as fuel depots, analysis labs and even hotels.
So, we see house infrastructure as the following large sector. The concern is, how do we generate the exact same economic efficiencies to private place stations like what Elon Musk is producing with reusable rockets?
In an perfect state of affairs, how would an Outpost mission work?Â
Marsh: A single use circumstance we are envisioning—and this is a few years in the long term, at least—is that just after a second phase is divided in room, it turns into an outpost. A little motor vehicle would then be deployed off of the outpost. It goes out, captures particles, sends them back to the outpost, and deposits them inside of the higher stage.
We are also imagining that we could use innovative robotics to change that debris into some thing useful.
Which phase is the project at correct now? What is your timeline for the to start with operational start?
Marsh: The initial Outpost mission is likely to start inside the future number of decades. The early ones are likely to be incredibly rudimentary in terms of abilities.
Manber: We are not seeking at grabbing a discarded next stage and converting it just but. We might be capable to do that in a ten years, but for now we are focusing on modifying them on the floor right before they go into house.Â
A single place in which we actually have to advance is the human-robotic interface, or HRI, due to the fact we do not want the to start with human who lands on the moon to spend all their time on design.
We are doing the job with various robotic partners to accomplish that. For example, we are doing the job with ULA to build experience in extending the missions of their upper stage known as Centaur. Correct now, a rocket launch can charge any place from $50 million to $70 million. If we can display that you can increase missions, then you are leveraging existing belongings and not having to pay for a total start. All you have to sacrifice is a handful of hundred kilograms of gas, due to the fact you are going to require the fuel tank place to put in payloads for later use.
Our partners have demonstrated that it’s essentially a quite fantastic trade-off to sacrifice a very little fuel for a ton far more capacity.Â
You have a massive take a look at flight termed Mars Demo-1 coming up in June future 12 months. What particular things will be tested all through that mission and what details are you striving to get from it?Â
Manber: We will test how to robotically slice via metallic in place, which will be a very important part of changing a rocket higher stage. So, the major target of this is a swift review to see what it’s like to minimize via metal in the vacuum of room.
It’s wonderful how small we know about operating in house over and above a space station—building issues, manufacturing, living and doing work. It is however all quite new.
The following large step will be to determine out how to choose management of an upper stage right after it has concluded its major mission. We believe that will occur in 2022.
Are there any places other than converting rocket parts in house wherever the systems you are building could be applied if the Outpost job does not materialize or requires lengthier than predicted?
Marsh: The Outpost program is created in this kind of an impressive way that we can condition it as we go. So, if some capabilities advance quicker than many others, we can alter the improvement towards that. We could shift a minimal little bit closer toward robotics and additional absent from space particles mitigation if that wants to occur.
Manber: And even if this challenge has to transform instructions, a lot of all the capabilities we are developing could be made use of in remote and harmful Earth missions, these as cleaning nuclear squander and operating underneath the sea.
We a short while ago introduced an agriculture technological innovation (AgTech) innovation system in partnership with the authorities of the United Arab Emirates to incentivize using house research to enable green Earth’s deserts.
So we are checking out the use of technologies that will not only support us establish a environmentally friendly long term in house but also assistance Earth.